Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Demonstration of Recovery Annealing on 7-bits per Cell 3D Flash Memory at Cryogenic Operation for Bit Cost Scalability and Sustainability
July 19, 2023
The bit density of flash memory has been increased not only by planar shrink and 3D stacking, but also by multi-level cells[1], resulting in an exponential scaling of the cost to store one bit of data (bit cost). In particular, multi-level cells are highly effective in reducing bit cost because they can increase bit density while maintaining the same memory cell structure. We have previously found that the combination of single-crystal channels and cryogenic operation can significantly improve storage performance and achieve 7-bit cells (7 bits/cell), which we reported at an international memory technology conference[2].
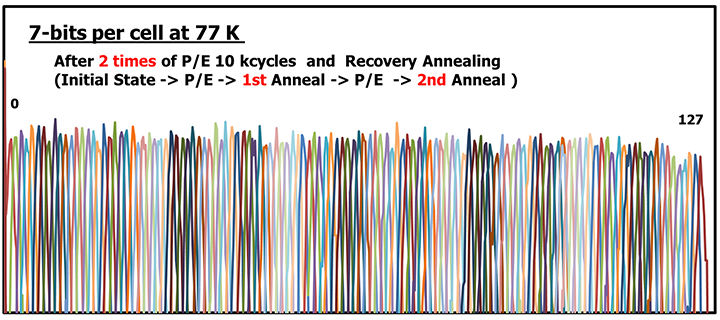
In this work, we examined the reusability of the memory by applying recovery treatment for further bit cost scaling toward the realization of sustainable society. Flash memory has a lifetime. Data is stored as the amount of electric charge in a memory cell, and during write/erase, a high voltage is applied to move charges in and out of a memory cell. The number of write/erase cycles is limited for SSDs, because it increases the noise during read cycle and decrease the data retention characteristics. We conducted an experiment to evaluate the storage performance degradation caused by write/erase cycles at cryogenic temperature and apply recovery annealing. As a result, we found that a relatively low temperature and short annealing time of 3 hours at 200°C with appropriate data written during annealing can fully recover memory cell characteristics. Furthermore, this recovery could be used repeatedly. We demonstrated the 7-bit cell operation after two times of write/erase cycles and recovery annealing (Figure 1). Even after a total 20k write/erase cycles, a tight distribution of 128 Vths (equivalent to 7 bits) was achieved, with performance equivalent to the initial state.
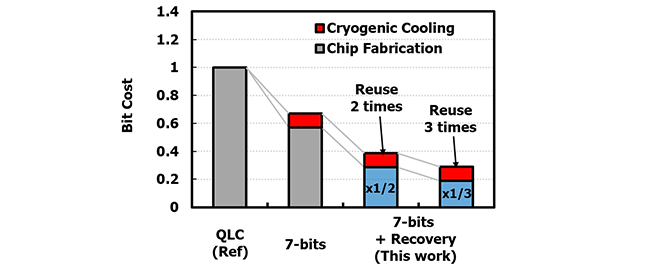
We estimated the storage system cost including the cryogenic cooling system. We believe that the combination of cryogenic operation and reuse by recovery annealing can reduce the bit cost by less than half compared to current QLCs, and this technology will make a significant contribution to realize a sustainable society (Figure 2).
This article is reconstructed from an excerpt of reference[3] presented at the VLSI Symposium (Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits) held in June 2023.
The cooling system for the cost evaluation was designed virtually by Nagase Techno-Engineering Co. Ltd.
Reference
[1] What is Multi-level Cell Technology Realizing Larger Capacity Flash Memory?
[2] H. Tanaka et al., IMW 2022, pp. 1-4.
[3] VLSI 2023 to be published

