Please select your location and preferred language where available.
“KioxiaSort” set a world record in the sort benchmark contest
May 19, 2020
In modern society, data sorting*1 is one of the essential techniques used in the area such as big data analysis and web searching. The sorting time is shortened by the progress of performance of computing systems, memories and storages as well as improvement of sorting algorithms.
On the other hand, energy problem is one of important issues of modern society, a large energy consumption due to increased computing power should be also taken care of. It becomes very important to reduce energy consumption as well as time for data sorting.
In sort benchmark contest*2 founded by Dr. Jim Gray who was a winner of ACM A.M. Turing Award*3, there is a category called JouleSort to compete energy consumption in data sorting. Our sorting algorithm KioxiaSort was awarded a JouleSort world record on November 27 in 2019.
KioxiaSort is based on classical external merge sort algorithm and consists of two main phases described in Fig. 1, Chunked Sort phase and Merge phase. Chunked Sort phase divides unsorted 1TB into many "chunks" so that each part can be stored and sorted in DRAM. Chunk means dividing a large file into many small parts. In the Merge phase after Chunked Sort phase, multiple sorted files are merged into final 1TB file maintaining the sorting relation among the files.
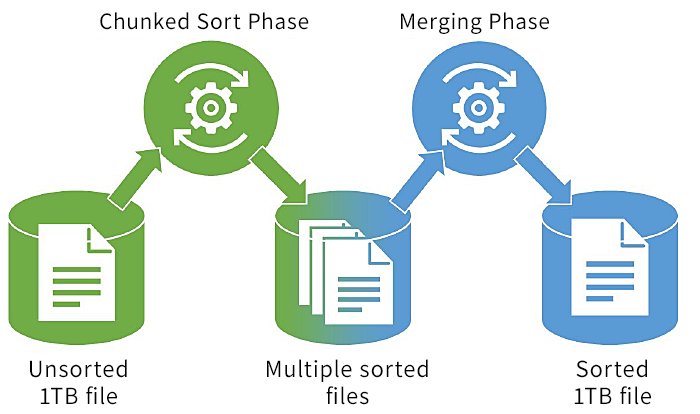
Figure 2 shows our measurement environment where a PC is connected with 9 SSDs implementing BiCS FLASH™. One of them is a Kioxia Client SSD XG5-P and is used as operating system (OS) drive.

A large-scale data sort requires efficient use of resources such as CPUs, DRAMs and SSDs. SSDs used to be system bottleneck, but nowadays CPUs and DRAMs are becoming critical as the performance of recent SSDs are greatly improved. Multi-threading*4 enables to shorten the executing time, resulting in reduction of energy which is the product of time and power. Moreover application of DMA*5 transfer reduces CPU load and brings out the performance of DRAM and SSD. As shown in Table 1, we achieved improvement of energy efficiency via these two techniques.
Table 1: Energy dependency on threading in Merging phase
|
Merging Phase (measured) |
Time (sec) |
Power (W) |
Energy (K Joules) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Single-thread |
1146 |
80.6 |
92.4 |
|
Multi-thread (8 threads) |
240 |
168.0 |
40.0 |
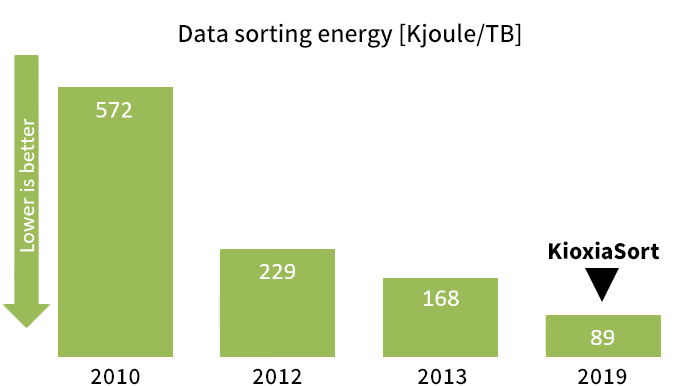
We ran KioxiaSort on the environment in Fig. 2 and accomplished only 89K Joules*6 for 1TB data sorting and significantly updated the previous records as shown in Fig. 3. It takes 8 minutes 45 seconds for 1TB data sorting, and storage throughput is as high as 7.6GB/sec*7.
We have achieved the energy efficient data sort which is one of basic techniques of modern society, utilizing the state of the art BiCS FLASH™ SSDs. Furthermore we have demonstrated the possibility to help solving energy issue toward AI and 5G era through the optimization of data sorting algorithm with SSDs.
We will continue the research and development of BiCS FLASH™ and related storage products in order to contribute to the society.
- To put elements of a list in a certain order.
- Refer to http://sortbenchmark.org/
- An annual prize given by ACM (Association for Computing Machinery) to an individual who has made innovative contributions to the computing community
- An ability of a computer program to manage multiple requests at a time.
(Single-tread manages only one request at a time) - Direct Memory Access, a feature to access main system memory directly without processing of CPU
- A unit of energy. 1 Joule equals to 1 Watt*Second
- Refer to http://sortbenchmark.org/KioxiaSort2019.pdf
Company names, product names, and service names may be trademarks of their respective companies.

