Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Storage Solutions Empowering AI


March 17, 2025
Generative AI use is rapidly expanding and growing, delivering innovative breakthroughs across many industries through systems that utilize natural language processing and image generation technologies. To be competitive, companies need fast and efficient data processing capabilities to best utilize the vast volumes of data for their AI models. Data storage and memory technologies are essential for high performance generative AI systems. Kioxia has a long-term commitment to advancing AI through industry contributions of research and development in flash memory, SSDs, and associated technologies.

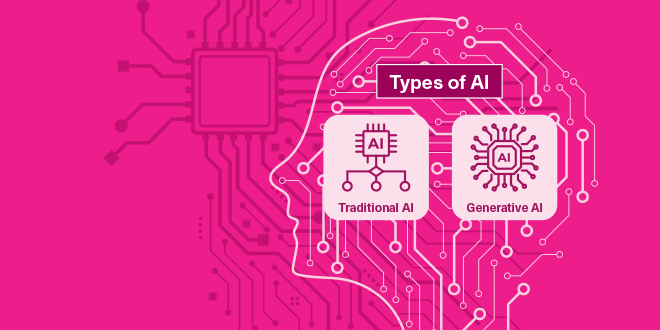
What is AI?
AI is technology that enables computer systems, using vast volumes of data, to perform tasks traditionally associated with human intelligence. Two prominent types are Traditional AI (responds to a set of inputs) and Generative AI (ability to create new data). Traditional AI is designed to perform predetermined tasks, recognizing and analyzing images and sounds based on learned data to predict outcomes. Generative AI, as the term “generative” implies, continuously enhances its learning process with deep learning, even incorporating information and data that hasn't been provided by humans, allowing it to create entirely new content.
Phases of AI and Storage Workload Requirements
In an AI system, there are phases such as data collection, transformation, learning, and inference to perform different AI functions, each with its corresponding workloads. These workloads put demands on core areas of the system, such as GPU, CPU, host memory and data storage. Data storage, typically SSDs and HDDs, must fulfill varied workload requirements.

Ingest
Import vast amounts of raw data to storage
Transform
Prepare data into proper formats for analysis, cleaning and validating
Storage saves formatted data and transfers it to the GPU server. Storage needs to have high capacity and high throughput (sequential read).
Training/Tuning
Process through AI algorithms, evaluate results and refine for accuracy
Storage saves intermediate results and caches training data. In the case of computation errors or system failures, snapshots are saved to avoid starting over from scratch. Since the GPU must be stopped during the snapshot process, high throughput is required to complete this process quickly.

Inference
Model recognizes new patterns and extrapolates conclusions
Data that has been added or updated after training, as well as highly confidential information, is stored in a separate database. Storage requires high capacity and high throughput (random read).
Kioxia's Activity for AI Technology
Kioxia has been conducting research and development in the field of AI for many years.
1. Autonomous Factories Utilizing AI
BiCS FLASH™ and other flash memories are fabricated at Kioxia’s Yokkaichi Plant, a smart factory that incorporates a broad array of cutting-edge manufacturing technologies. Big data are collected from manufacturing and test systems and are analyzed using machine learning and other AI technologies, which enhances productivity.
2. Research and Development of ‘Memory-Centric AI’ (AI using search)
Kioxia has authored research on the mechanisms for building and evaluating systems that combine Large Language Models (LLMs) with search.
Outlook for AI Industries and Data Storage ~ Maximizing Effectiveness of Generative AI in the Inference Era ~
Large Language Models (LLMs), which emerged at the end of 2022 and captured global attention, have triggered a major movement by “Big Tech” companies—companies developing world-changing technologies—in the field of learning and inference, which led to the dawn of generative AI. The services provided by LLMs are expected to be integrated into a wide range of business models, industries, and society.
To increase accuracy, relevance, and timeliness of inference, a novel approach known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged, designed to maximize the effectiveness of inference.
Utilizing SSDs in Generative AI systems (Learning/Inference)
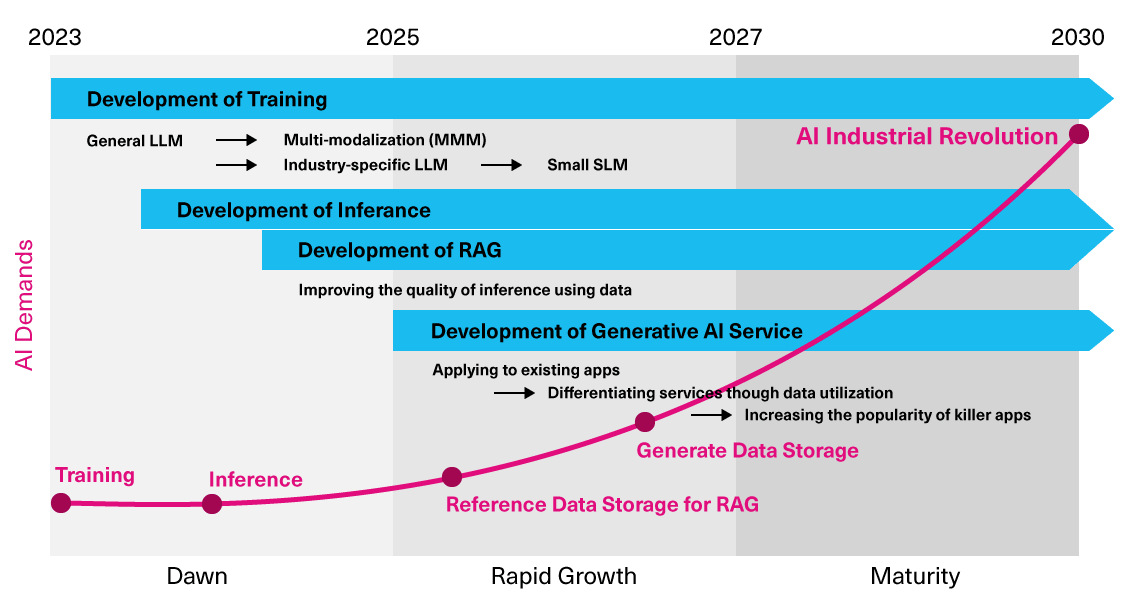
An essential element for any generative AI system is data. SSDs are becoming a more important way to store data with their characteristics of non-volatility, large capacity, and high speed. SSDs are evolving with the different stages of generative AI, and as a result, the demand for SSDs is rapidly increasing. It is expected that between 2024 and 2030, the market for SSD capacity will grow significantly, approximately 40 to 50 times.
Kioxia believes the medium to long term outlook through 2030, growth of the generative AI market will be driven by the following four trends:
- Development of learning
- Development of inference
- Development of RAG for enhanced inference
- Development of generative AI services
SSDs are expected to play a pivotal role in all of these trends.
SSD Advantages from a hardware perspective
In generative AI systems, expensive GPUs are used for both training and inference, and it is difficult to address the large quantities of data required for the generative AI process using only volatile DRAM. Therefore, data processing becomes essential for tasks such as supplying training data from non-volatile storage devices, referencing data for RAG during inference, and storing generated data.
An important requirement for storage devices now is to help maximize GPU utilization and get the most out expensive GPUs, as well as to maximize power and space efficiency. HDDs come to mind when thinking of large storage capacities, however, they are limited by their mechanical characteristics, such as media rotation delay and the movement of read/write heads. This results in read/write latencies that can be over 100 times higher than SSDs, which impacts overall power efficiency. SSDs support AI storage services to maximize processing efficiency of high-performance GPUs, and will meet the demand for increasingly larger capacities in the future.
Advantages of SSD for inference demand
LLMs are already being used by many companies to improve operational efficiency and productivity.
But the knowledge possessed by LLMs is limited to the data set used during training, which may be out of date. An older LLM might not generate accurate results for questions or instructions requiring the latest, company proprietary, or confidential information not available to the LLM. These inaccurate results, which are sometimes way off track, are called hallucinations.
RAG solves the hallucination problem by incorporating more accurate knowledge and data outside of the LLM in the form of a vector database. RAG uses database software with a data retrieval function based on vector similarity, called a vector database. Many companies are interested in RAG because it can enhance LLM capabilities utilizing non-public information to improve the accuracy of the AI model.
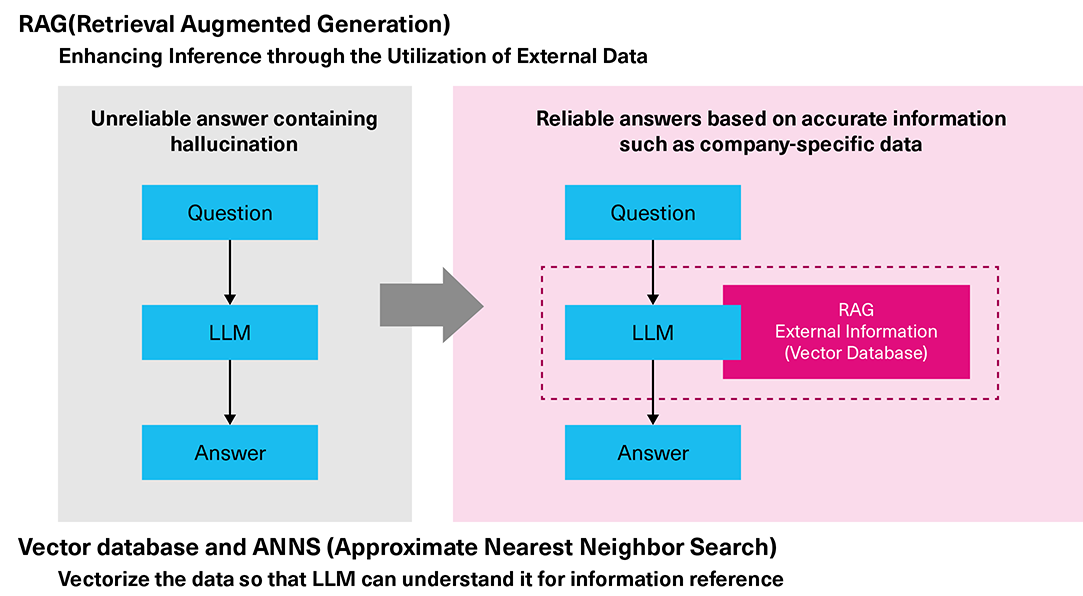
In RAG, locating the vector closest to the query vector (and the corresponding data among the stored knowledge data) involves calculating the similarity between high-dimensional vectors that can range from hundreds to thousands of dimensions. It is an intensive task even for the latest AI servers. To address this challenge, approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search can be used with an index to narrow down the comparison vectors to a small number of vectors, to find an approximate solution.
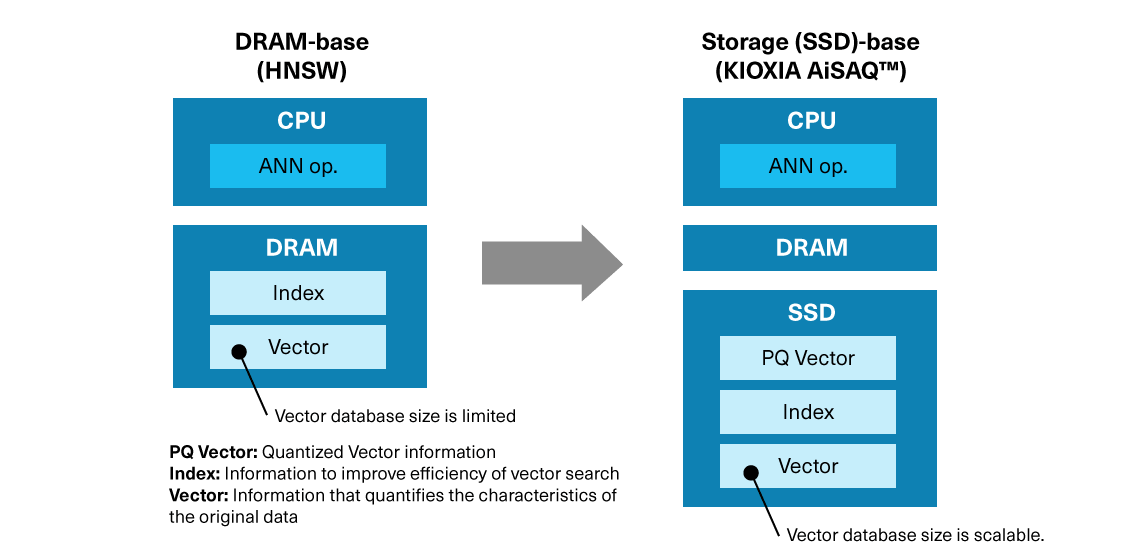
There are various methods for ANN searches, including DRAM-based Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) and DiskANN, developed by Microsoft, which is primarily storage-based. Currently, HNSW, which stores vectors and indices in DRAM, is widely used. In this method, the number of vectors, which is the volume of knowledge it can utilize, is limited by the amount of DRAM in the server, thus limiting the ability to build increasingly effective RAG systems built on large volumes of knowledge.
Kioxia has developed KIOXIA AiSAQ™ software as a new ANN storage method utilizing SSDs. To further leverage SSDs, especially in the rapidly growing generative AI market, Kioxia will continue advancing its research and development of this important storage technology.
KIOXIA AiSAQ™ Technology: An AI innovation developed by Kioxia
KIOXIA AiSAQ™ (All-in-Storage ANNS with Product Quantization) software, as the name suggests, transfers information that quantizes data characteristics (PQ data) and all ANN elements to SSD storage to optimize approximate nearest neighbor search algorithms for vector search processing in the RAG phase. It has been released as open source to enable higher quality generative AI applications for the market.
In an AI workflow, indexed data is typically stored in DRAM to enhance the efficiency of vector searches. KIOXIA AiSAQ™ technology places indexed data on SSDs.
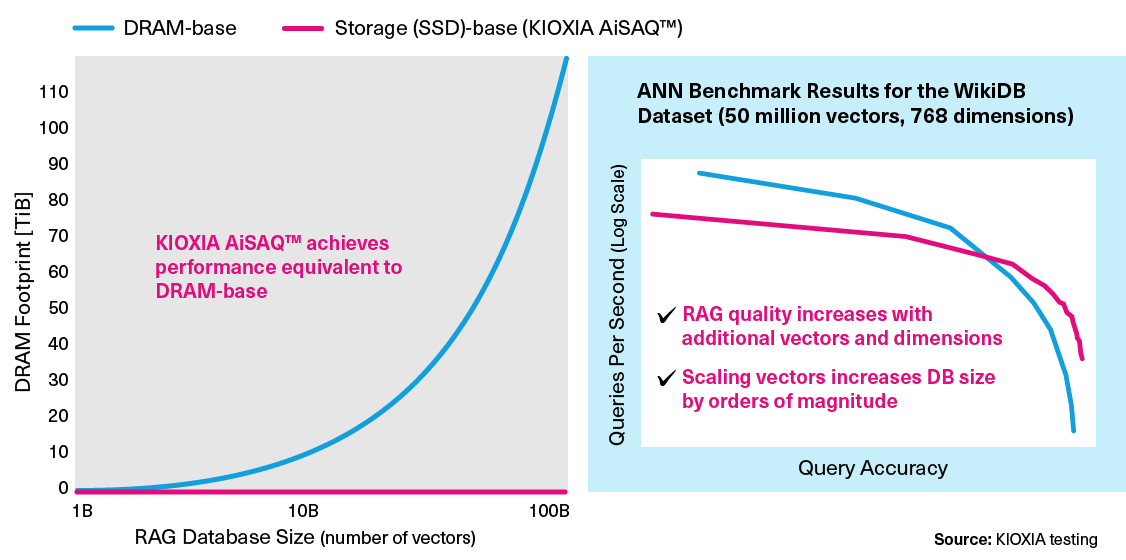
For more accurate AI queries, RAG vector databases will grow and scale. For the DRAM-based approach, larger databases require more DRAM (graph on the left in the figure below). From a performance perspective, SSD-based search outperforms DRAM-based search in terms of query accuracy and queries per second (graph on the right in the figure below).
This innovative RAG technology is promising because it uses less expensive SSDs, rather than costly DRAM to improve ANNS without compromising performance.
KIOXIA AiSAQ™ Software Download
KIOXIA AiSAQ™ software is open-source. Please follow the link to download.
GitHub:

KIOXIA Products Supporting the AI Market
Introducing KIOXIA Enterprise and Data Center SSDs for AI workloads.

- Definition of capacity: KIOXIA Corporation defines a megabyte (MB) as 1,000,000 bytes, a gigabyte (GB) as 1,000,000,000 bytes and a terabyte (TB) as 1,000,000,000,000 bytes. A computer operating system, however, reports storage capacity using powers of 2 for the definition of 1 GB = 2^30 = 1,073,741,824 bytes and therefore shows less storage capacity. Available storage capacity (including examples of various media files) will vary based on file size, formatting, settings, software and operating system, and/or pre-installed software applications, or media content. Actual formatted capacity may vary.
- NVMe is a registered or unregistered mark of NVM Express, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
- PCIe and PCI Express are registered trademarks of PCI-SIG.
- Other company names, product names, and service names may be trademarks of third-party companies.


